Often we may want to calculate the variance of a grouped frequency distribution.
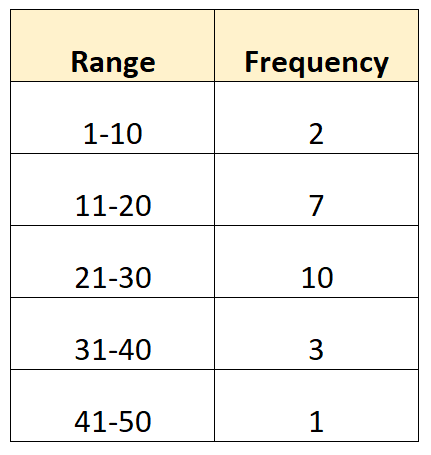
For example, suppose we have the following grouped frequency distribution:
While it’s not possible to calculate the exact variance since we don’t know the raw data values, it is possible to estimate the variance using the following formula:
Variance: Σni(mi-μ)2 / (N-1)
where:
- ni: The frequency of the ith group
- mi: The midpoint of the ith group
- μ: The mean
- N: The total sample size
Note: The midpoint for each group can be found by taking the average of the lower and upper value in the range. For example, the midpoint for the first group is calculated as: (1+10) / 2 = 5.5.
The following example shows how to use this formula in practice.
Example: Calculate the Variance of Grouped Data
Suppose we have the following grouped data:
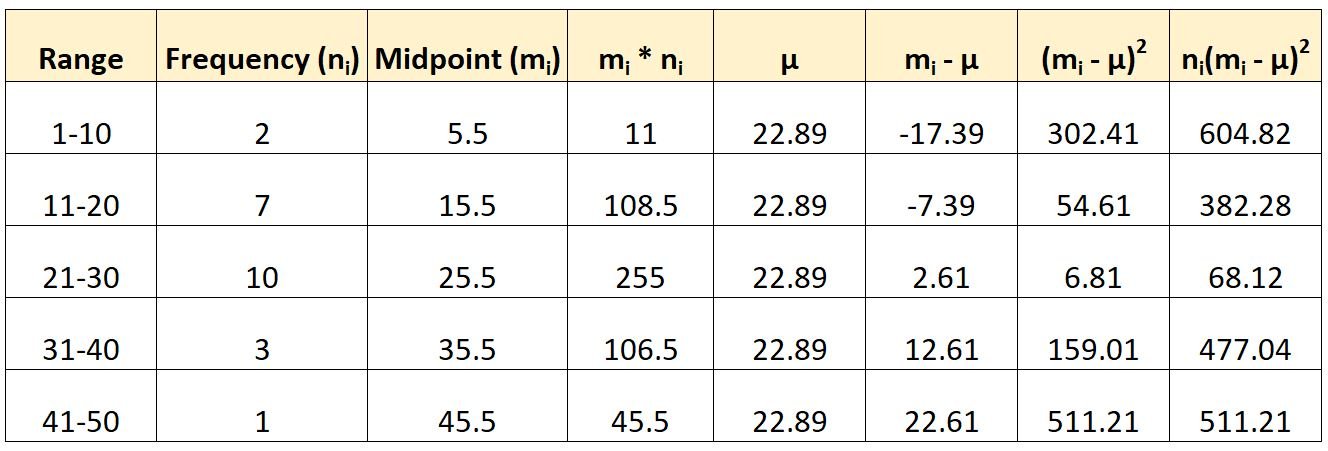
Here’s how we would use the formula mentioned earlier to calculate the variance of this grouped data:
We would then calculate the variance as:
- Variance: Σni(mi-μ)2 / (N-1)
- Variance: (604.82 + 382.28 + 68.12 + 477.04 + 511.21) / (23-1)
- Variance: 92.885
The variance of the dataset turns out to be 92.885.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to calculate other metrics for grouped data:
How to Find Mean & Standard Deviation of Grouped Data
How to Calculate Percentile Rank for Grouped Data
How to Find the Median of Grouped Data
How to Find the Mode of Grouped Data