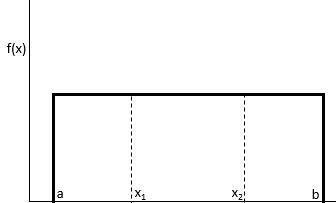
A uniform distribution is a probability distribution in which every value between an interval from a to b is equally likely to be chosen.
The probability that we will obtain a value between x1 and x2 on an interval from a to b can be found using the formula:
P(obtain value between x1 and x2) = (x2 – x1) / (b – a)
To calculate probabilities related to the uniform distribution in Python we can use the scipy.stats.uniform() function, which uses the following basic syntax:
scipy.stats.uniform(x, loc, scale)
where:
- x: The value of the uniform distribution
- loc: The minimum possible value
- loc + scale: The maximum possible value
The following examples show how to use this function in practice.
Example 1
Suppose a bus shows up at a bus stop every 20 minutes. If you arrive at the bus stop, what is the probability that the bus will show up in 8 minutes or less?
We can use the following code in Python to calculate this probability:
from scipy.stats import uniform #calculate uniform probability uniform.cdf(x=8, loc=0, scale=20) - uniform.cdf(x=0, loc=0, scale=20) 0.4
The probability that the bus shows up in 8 minutes or less is 0.4.
Example 2
The weight of a certain species of frog is uniformly distributed between 15 and 25 grams. If you randomly select a frog, what is the probability that the frog weighs between 17 and 19 grams?
We can use the following code in Python to calculate this probability:
from scipy.stats import uniform #calculate uniform probability uniform.cdf(x=19, loc=15, scale=10) - uniform.cdf(x=17, loc=15, scale=10) 0.2
The probability that the frog weighs between 17 and 19 grams is 0.2.
Example 3
The length of an NBA game is uniformly distributed between 120 and 170 minutes. What is the probability that a randomly selected NBA game lasts more than 150 minutes?
We can use the following code in Python to calculate this probability:
from scipy.stats import uniform
#calculate uniform probability
uniform.cdf(x=170, loc=120, scale=50) - uniform.cdf(x=150, loc=120, scale=50)
0.4
The probability that a randomly selected NBA game lasts more than 150 minutes is 0.4.
Bonus: You can double check the solution to each example by using the Uniform Distribution Calculator.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to use other common distributions in Python:
How to Use the Binomial Distribution in Python
How to Use the Poisson Distribution in Python
How to Use the t Distribution in Python