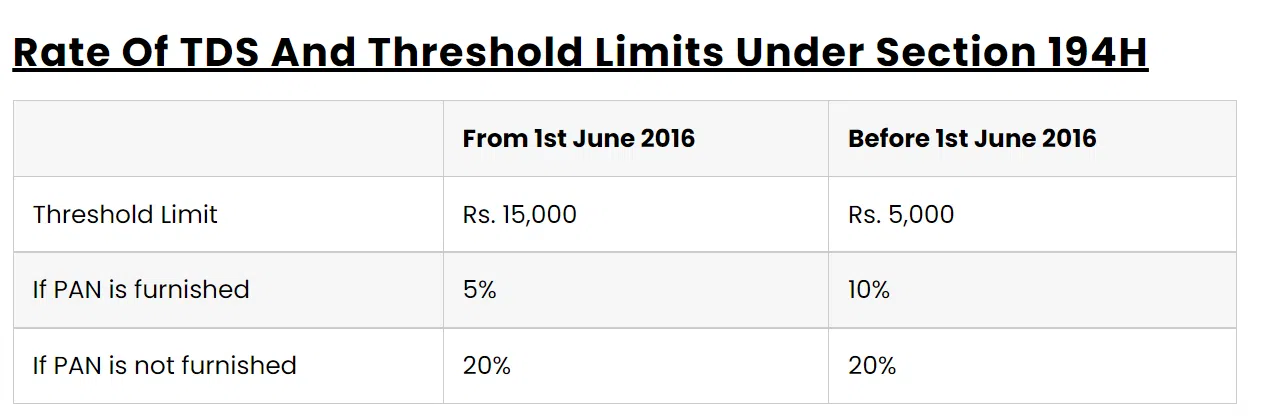
There are several criterias when it comes to Section 194H TDS on commission and brokerage. Income tax withheld by the person responsible for paying the resident with commission or brokerage is subject to Section 194H. Individuals and undivided Hindu families must deduct TDS based on Section 44AB. Authorised entities can deduct TDS, and this is not possible for singles or HUF (Hindu Undivided Family). The 194H deduction threshold is ₹15,000. If revenue is credited to the recipient’s account or another account, TDS will be deducted according to Section 194H.
Did you know?
Section 194H of the Income-tax Act allows businesses to deduct excess TDS at a rate of 20% or 30%. Prior to the change, Indian companies could only claim a 10% or 20% tax credit, resulting in higher costs. This led to clashes between the government and various corporations like Bharati Airtel.
Section 194H applies to income tax withheld by the person responsible for paying commissions or brokerage revenue to the resident. Section 44AB also requires individuals and undivided Hindu households to deduct TDS. Individuals with business incomes over ₹1crore, HUF total income exceeding ₹5,00,000, or vocations exceeding ₹5,00,000 must be kept by TDS starting in 2020-21.
Premiums paid under Section 194D are not included in Section 194H, and TDS on fees or brokerage gains are dealt with under Section 194H of the Income Tax Act. The sum paid to a corporation for providing services at the time of sale or purchase is known as commission. This tax applies to both individuals and HUFs. Anyone earning more than ₹15,000 per year is also affected. The most crucial documents for TDS deductions are deductible TANs and deductible PANs.
Also Read: Guide On TDS Payment To Contractor (Section 194C)
When Does TDS Under Section 194H Need To Be Deducted?
TDS will be deducted if revenue is deposited to the recipient’s or another account in accordance with Section 194H. When money is moved to the recipient’s account or when the recipient’s account is closed, TDS must be deducted. When a banned or unnamed account is credited, this amount is considered credited to the recipient’s account and must be deducted from TDS at the time of credit.
What Do You Mean By Commission And Brokerage?
“Commission or brokerage,” defined by Section 194H, is money earned or obtained indirectly from someone for acting on behalf of another person for the following purposes: except for professional services, all services are given. All services here pertain to the acquisition or sale of merchandise. Section 194H applies to income tax withheld by the person responsible for paying the resident’s fees or brokerage revenue. Section 44AB also requires individuals and undivided Hindu households to deduct TDS. The TDS rate for commissions, also known as brokerage commissions, has increased from 5% to 10% in 2016-2017. There are no additional taxes or education taxes on payments to residents. If the recipient does not provide a PAN, TDS will be deducted at a rate of 20%.
What is the Rate of TDS?
TDS rate charts range from 10% to 30% and are calculated depending on an individual’s wage. With the TDS rate for this year’s revenue, the TDS rate chart for the fiscal year 2020-21 has been updated.
TDS stands for tax withholding. The Indian government employs an indirect method to collect tax withholding. The Central Direct Tax Board is in charge of the TDS (CBTD). Bonuses and commissions, dividends, payments for various services, real estate sales, rents, purchases, time deposits, and other sources of income are all subject to TDS. TDS is deducted at different rates depending on the source of income, ranging from 1% to 30%. The person responsible for the tax credit must do this at a reasonable tax rate and remit the deduction to the Government of India.
Under What Circumstances, TDS U/S 194H Is Not Deductible
- If the entire amount of such income assessed or paid during the fiscal year does not exceed ₹15,000, deductions are not allowed. Article 197 will enable individuals to apply to an appraiser for zero or less tax credit. BSNL/MTNL pays public call centre franchise referral fees or commissions.
- TDS is not required to be deducted if the payer is a person or a HUF who does not need to verify the account. Individuals and HUFs who pay monthly rents of ₹50,070 or more must deduct 5% TDS, even if they are not subject to a tax audit.
Also Read: Time Limit To Deposit TDS And File TDS Return
What Is The Time Limit On Depositing TDS?
Taxes must be deposited by the 7th of the next month from April to February. Tax credits for March must be submitted by April 30th. After deducting the TDS from the payment, the payer must deposit the withholding tax into the government account as soon as feasible. TDS is withdrawn, and he remains on bail. The payer just represents the government. This is not his earnings, and it must be remitted to the government on time. Taxes withheld on April 25 must be reported by May 7, and taxes withheld on March 15 must be submitted by April 30.
Conclusion
This article provides comprehensive information about Section 194H of the Income Tax Act. Section 194H relates to income tax deducted from those obliged to pay the resident with commission or brokerage income. Individuals covered by Section 44AB and undivided Hindu families must also deduct TDS. If the total income from individuals and HUFs with business sales of over ₹1 crore or from occupations exceeds ₹5,00,000, TDS must be deducted from 2021. We also considered when it applies and when it does not. We also found out why it is not applicable in certain cases. Knowing the deadline for submitting TDS is also very important. After deducting TDS from the payment amount, the payer must deposit the withholding tax in the government account as soon as possible. In the case of TDS, he withdraws and holds the deposit. The payer acts only on behalf of the government. This is not his income and must be paid to the government on time.
Follow Legal Tree for the latest updates, articles, and news blogs related to medium, small, and micro-businesses (MSMEs), business tips, income tax, GST, salary, and accounting.