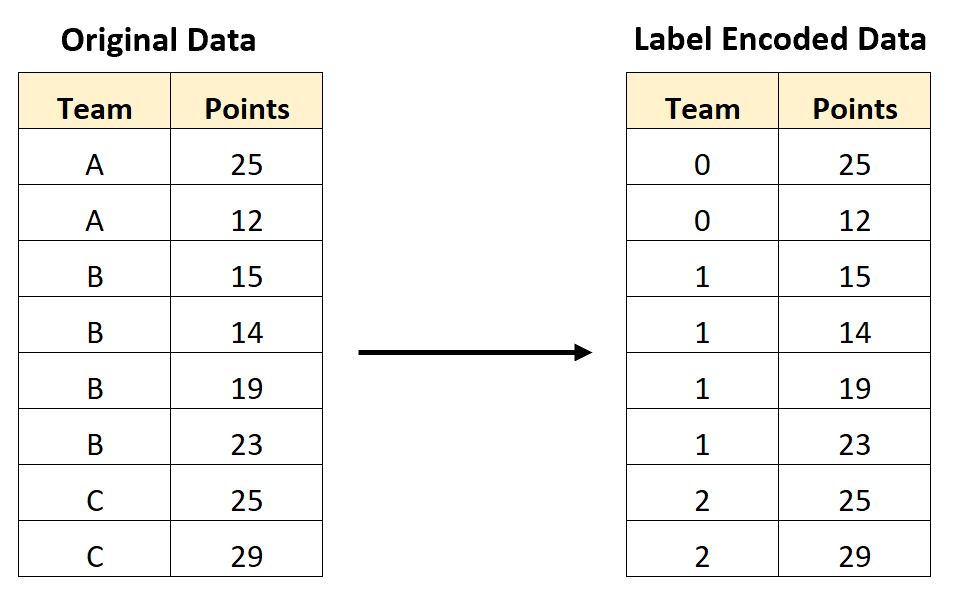
Often in machine learning, we want to convert categorical variables into some type of numeric format that can be readily used by algorithms.
One way to do this is through label encoding, which assigns each categorical value an integer value based on alphabetical order.
For example, the following screenshot shows how to convert each unique value in a categorical variable called Team into an integer value based on alphabetical order:
There are two common ways to perform label encoding in R:
Method 1: Use Base R
df$my_var numeric(factor(df$my_var))
Method 2: Use CatEncoders Package
library(CatEncoders) #define original categorical labels labs = LabelEncoder.fit(df$my_var) #convert labels to numeric values df$team = transform(labs, df$my_var)
The following examples show how to use each method in practice.
Example 1: Label Encoding Using Base R
The following code shows how to use the factor() function from base R to convert a categorical variable called team into a numeric variable:
#create data frame df frame(team=c('A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'), points=c(25, 12, 15, 14, 19, 23, 25, 29)) #view data frame df team points 1 A 25 2 A 12 3 B 15 4 B 14 5 B 19 6 B 23 7 C 25 8 C 29 #perform label encoding on team variable df$team numeric(factor(df$team)) #view updated data frame df team points 1 1 25 2 1 12 3 2 15 4 2 14 5 2 19 6 2 23 7 3 25 8 3 29
Notice the new values in the team column:
- “A” has become 1.
- “B” has become 2.
- “C” has become 3.
We have successfully converted the team column from a categorical variable into a numeric variable.
Example 2: Label Encoding Using CatEncoders Package
The following code shows how to use functions from the CatEncoders() package to convert a categorical variable called team into a numeric variable:
library(CatEncoders) #create data frame df frame(team=c('A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'), points=c(25, 12, 15, 14, 19, 23, 25, 29)) #define original categorical labels labs = LabelEncoder.fit(df$team) #convert labels to numeric values df$team = transform(labs, df$team) #view updated data frame df team points 1 1 25 2 1 12 3 2 15 4 2 14 5 2 19 6 2 23 7 3 25 8 3 29
Once again, we have generated the following new values in the team column:
- “A” has become 1.
- “B” has become 2.
- “C” has become 3.
This matches the results from the previous example.
Note that using this method, you can also use inverse.transform() to obtain the original values from the team column:
#display original team labels inverse.transform(labs, df$team) [1] "A" "A" "B" "B" "B" "B" "C" "C"
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in R:
How to Create Categorical Variable from Continuous in R
How to Create Categorical Variables in R
How to Convert Categorical Variables to Numeric in R