In statistics, we’re often interested in knowing how “spread out” the values are in a distribution.
One popular way to measure spread is the interquartile range, which is calculated as the difference between the first quartile and the third quartile in a dataset. Quartiles are simply values that split up a dataset into four equal parts.
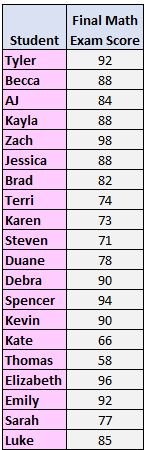
Example: Calculating the Interquartile Range
The following example shows how to calculate the interquartile range for a given dataset:
Step 1: Arrange the values from smallest to largest.
58, 66, 71, 73, 74, 77, 78, 82, 84, 85, 88, 88, 88, 90, 90, 92, 92, 94, 96, 98
2. Find the median.
58, 66, 71, 73, 74, 77, 78, 82, 84, 85, 88, 88, 88, 90, 90, 92, 92, 94, 96, 98
In this case, the median is between 85 and 88.
3. The median splits the dataset into two halves. The median of the lower half is the lower quartile and the median of the upper half is the upper quartile:
58, 66, 71, 73, 74, 77, 78, 82, 84, 85, 88, 88, 88, 90, 90, 92, 92, 94, 96, 98
4. Calculate the interquartile range.
In this case, the first quartile is the average of the middle two values in the lower half of the data set (75.5) and the third quartile is the average of the middle two values in the upper half of the data set (91).
Thus, the interquartile range is 91 – 75.5 = 15.5
The Interquartile Range is Not Affected By Outliers
One reason that people prefer to use the interquartile range (IQR) when calculating the “spread” of a dataset is because it’s resistant to outliers. Since the IQR is simply the range of the middle 50% of data values, it’s not affected by extreme outliers.
To demonstrate this, consider the following dataset:
[1, 4, 8, 11, 13, 17, 17, 20]
Here are the various measures of spread for this dataset:
- Interquartile range: 11
- Range: 19
- Standard deviation: 6.26
- Variance: 39.23
Now, consider the same dataset but with an extreme outlier added to it:
[1, 4, 8, 11, 13, 17, 17, 20, 150]
Here are the various measures of spread for this dataset:
- Interquartile range: 12.5
- Range: 149
- Standard deviation: 43.96
- Variance: 1,932.84
Notice how the interquartile range changes only slightly, from 11 to 12.5. However, all of the other measures of dispersion change drastically.
This demonstrates that the interquartile range is not affected by outliers like the other measures of dispersion. For this reason, it’s a reliable way to measure the spread of the middle 50% of values in any distribution.
Further Reading:
Measures of Dispersion
Interquartile Range Calculator