You can use the following basic syntax to add a line that represents the average value in a plot in ggplot2:
ggplot(df, aes(x=x, y=y)) + geom_point() + geom_hline(yintercept = mean(df$y, na.rm=TRUE))
The following example shows how to use this syntax in practice.
Example: Add Average Line to Plot in ggplot2
Suppose we have the following data frame in R:
#create data frame df frame(x=c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12), y=c(2, 5, 6, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12, 10, 9, 11, 15)) #view head of data frame head(df) x y 1 1 2 2 2 5 3 3 6 4 4 5 5 5 7 6 6 8
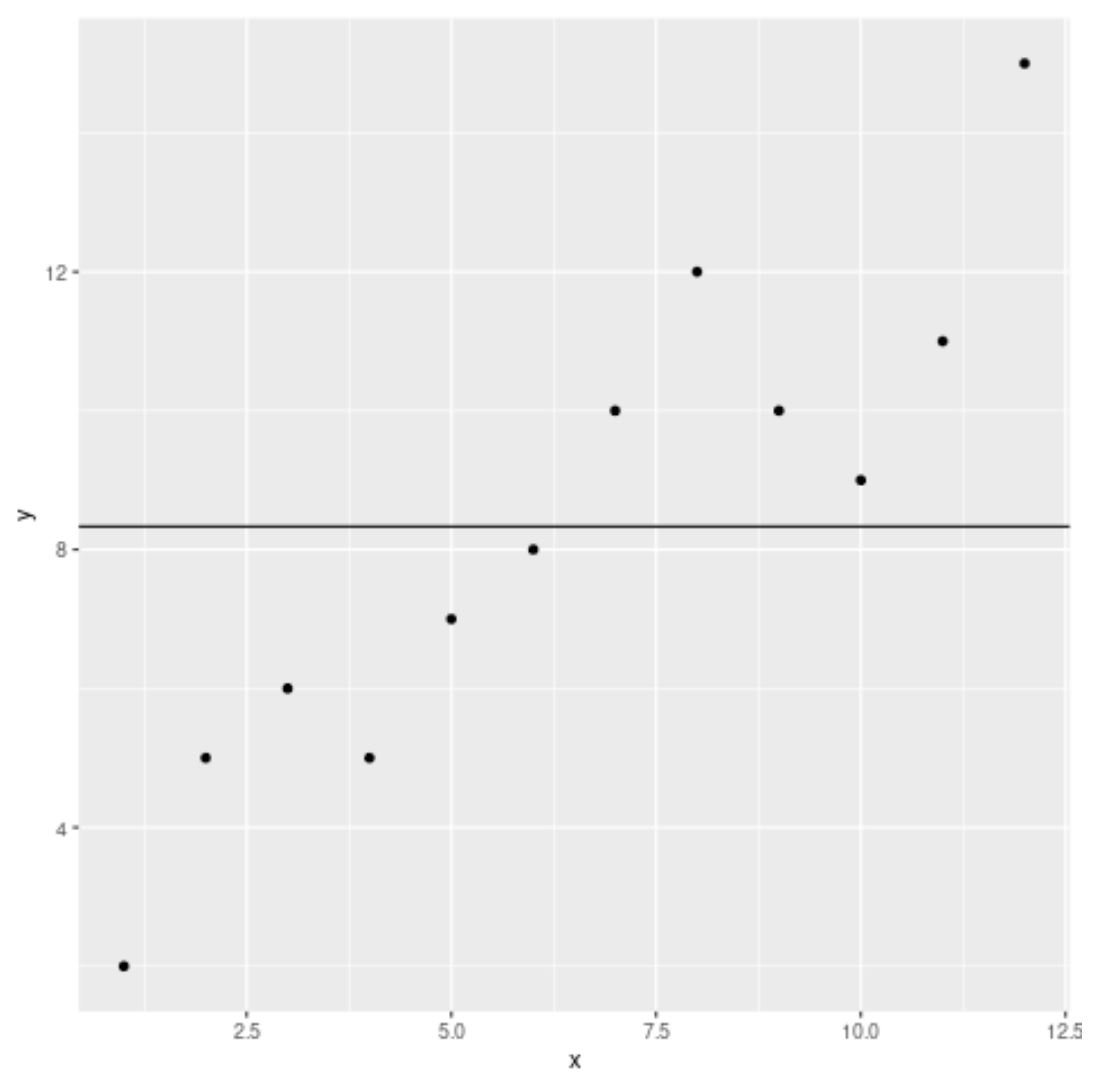
We can use the following code to create a scatter plot of x vs. y and add a horizontal line that represents the average y-value:
library(ggplot2) #create scatter plot with average line to represent average y-value ggplot(df, aes(x=x, y=y)) + geom_point() + geom_hline(yintercept = mean(df$y, na.rm=TRUE))
We can see that an average line has been added to the plot just above the y-value of 8.
If we calculate the average y-value, we’ll find that it’s 8.333:
#calculate average y-value mean(df$y, na.rm=TRUE) [1] 8.333333
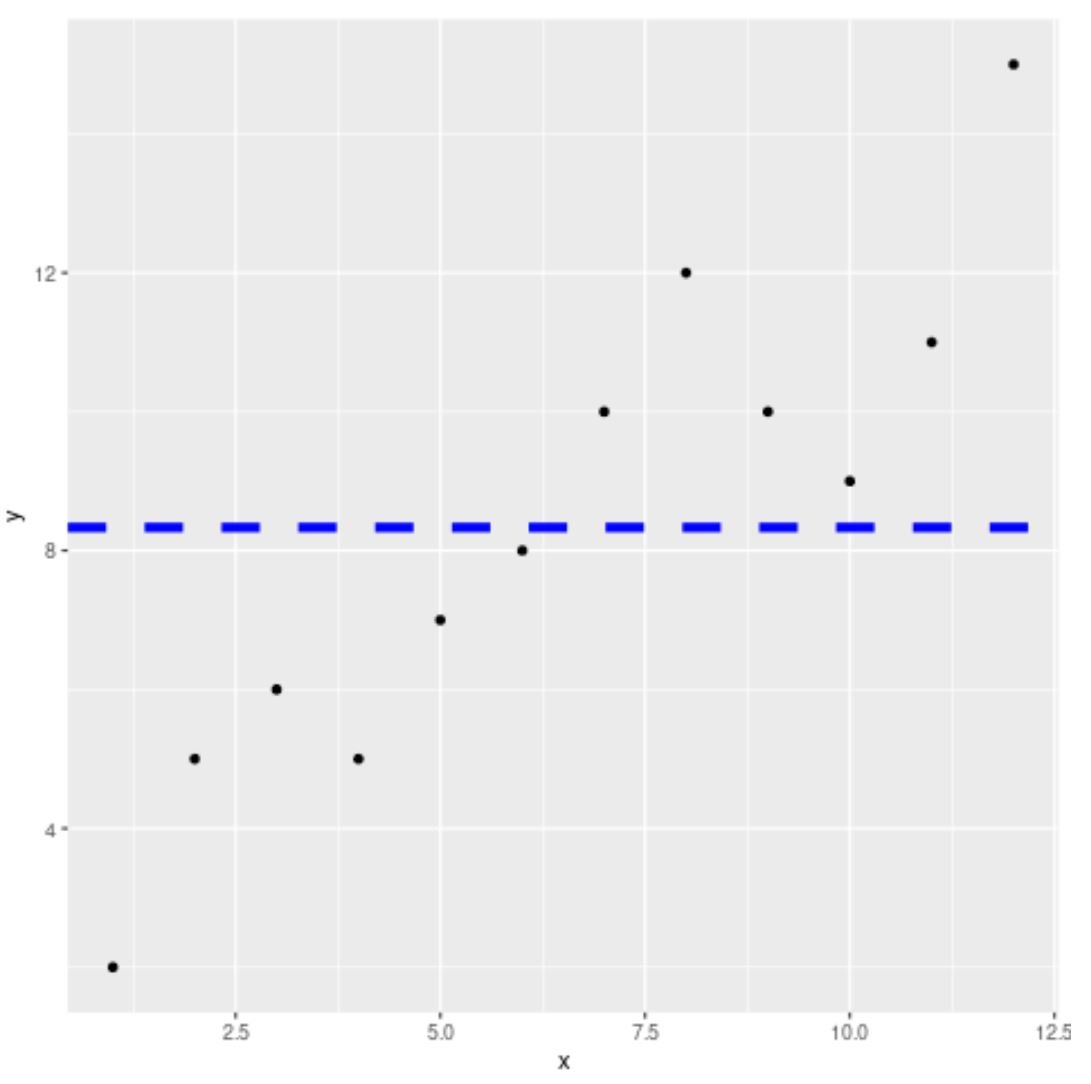
Note that we can also use the color, lty, and lwd arguments to specify the color, line type, and line width of the average line, respectively:
library(ggplot2) #create scatter plot with custom average line ggplot(df, aes(x=x, y=y)) + geom_point() + geom_hline(yintercept = mean(df$y, na.rm=TRUE), color='blue', lty='dashed', lwd=2)
The average line is now blue, dashed, and has a line width of 2.
You can find the complete online documentation for the geom_hline() function here.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in ggplot2:
How to Draw a Trend Line in ggplot2
How to Adjust Line Thickness in ggplot2
How to Set Axis Limits in ggplot2