You can use the following basic syntax to perform a VLOOKUP from another workbook in Excel:
=VLOOKUP(A2,'[data2.xlsx]Sheet1'!$A$1:$B$11,2,0)
This particular formula will look up the value in cell A2 of the current workbook in the range A1:B11 of a second workbook called data2.xlsx and return the corresponding value in the second column.
Note: For this formula to work, both workbooks should be saved in the same directory.
The following step-by-step example shows how to use this formula in practice.
Step 1: Enter Data into Both Workbooks
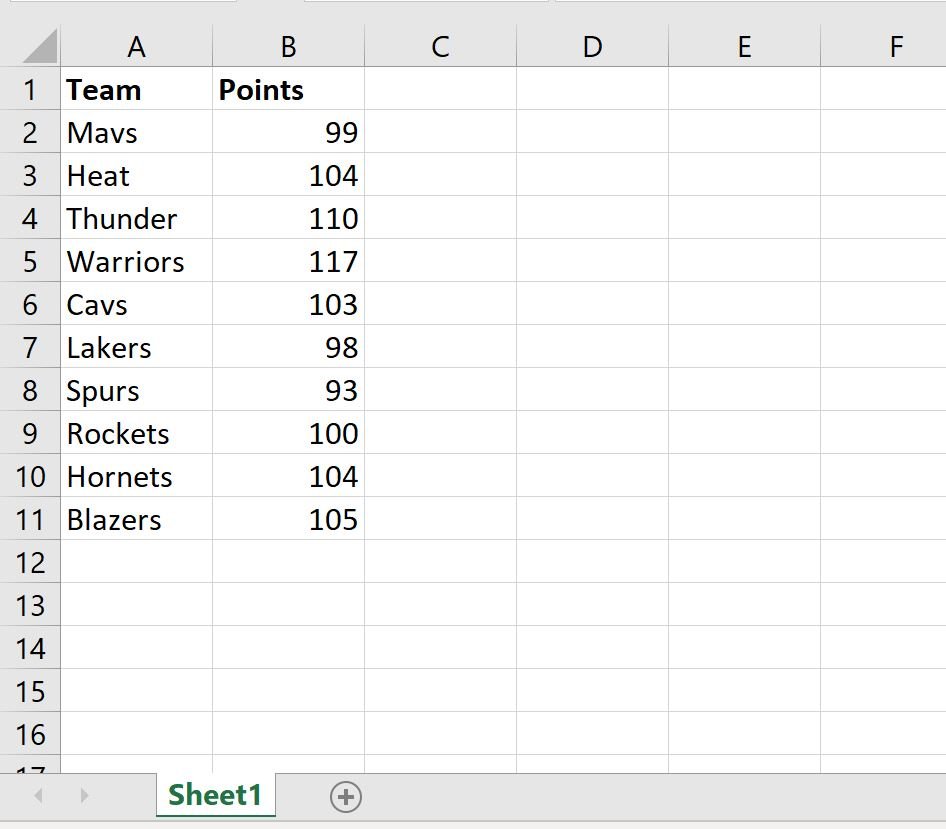
Suppose we have the following workbook called data.1.xlsx:
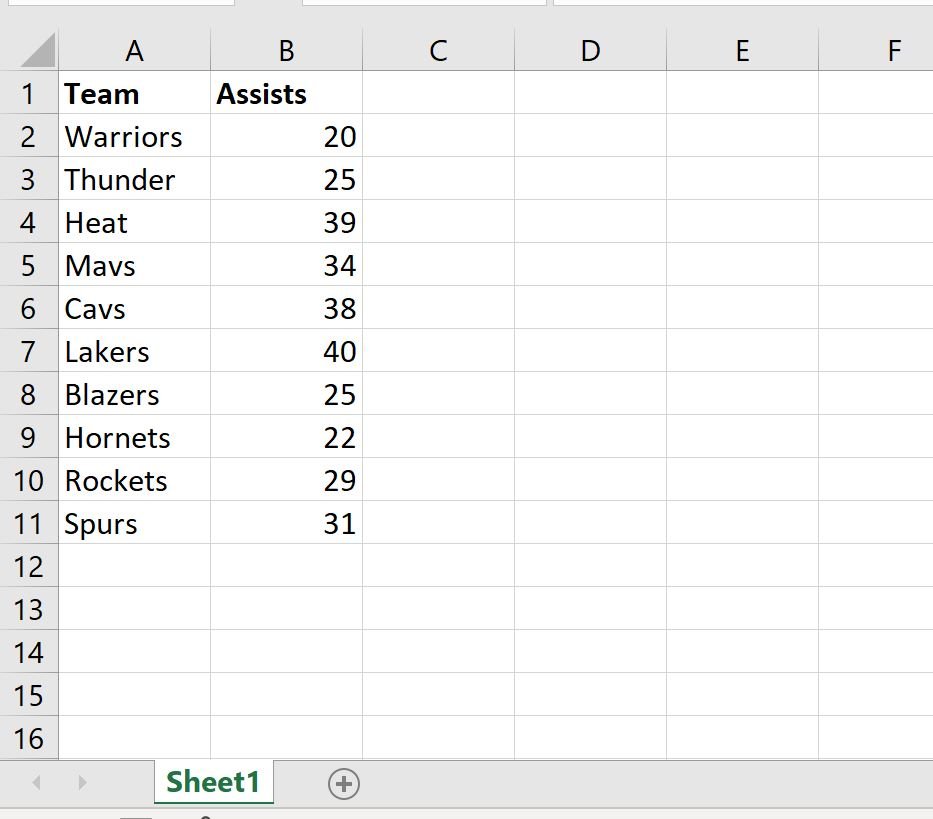
And suppose we have another workbook called data2.xlsx:
Both workbooks are saved in the same directory.
Step 2: Perform VLOOKUP Between Workbooks
Now suppose we would like to use a VLOOKUP in the first workbook to look up the team names in the second workbook and return the corresponding value in the Assists column.
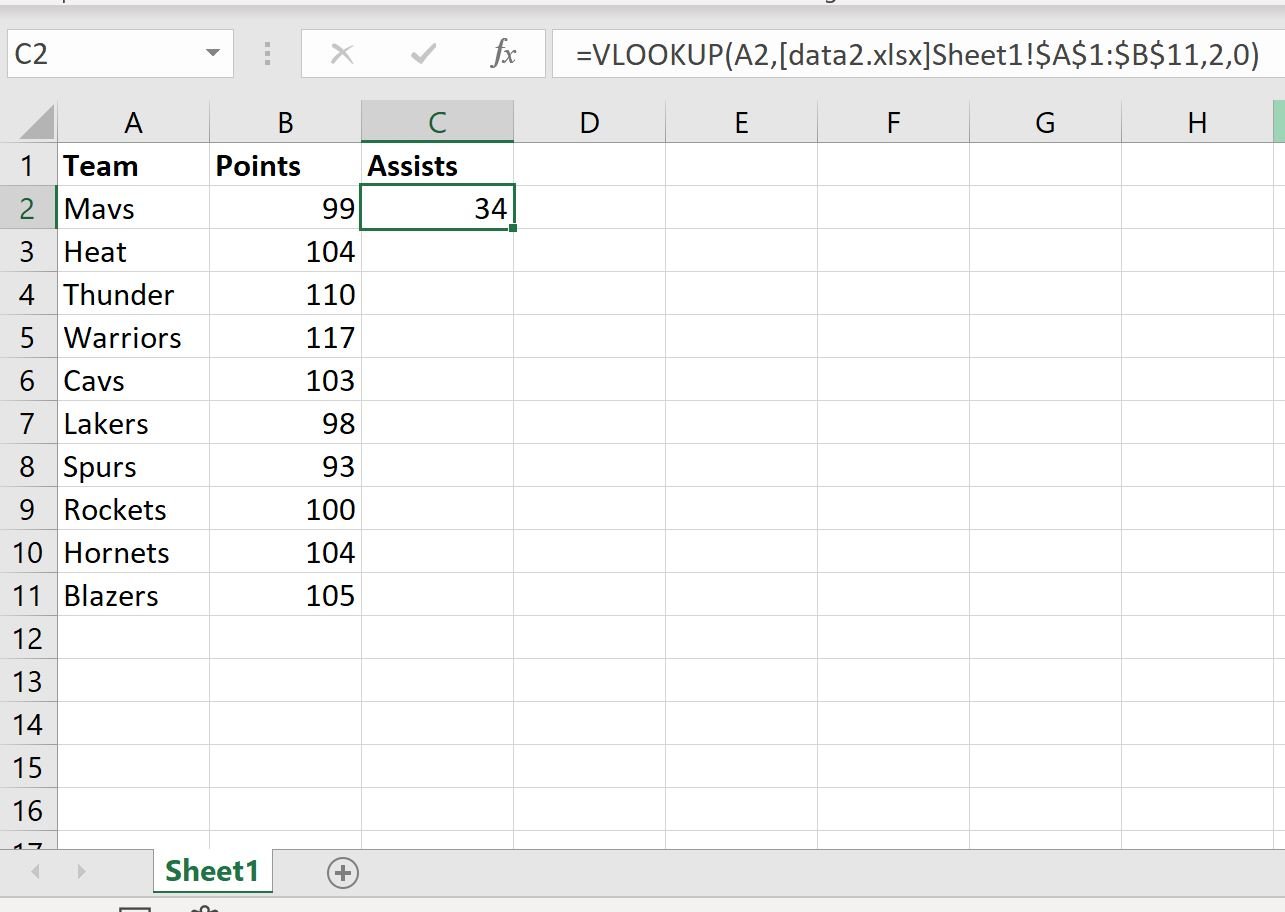
To do so, we can type the following formula into cell C2 of the first workbook:
=VLOOKUP(A2,'[data2.xlsx]Sheet1'!$A$1:$B$11,2,0)
Once we press Enter, the value in the Assists column from the second workbook that corresponds to the “Mavs” team will be shown:
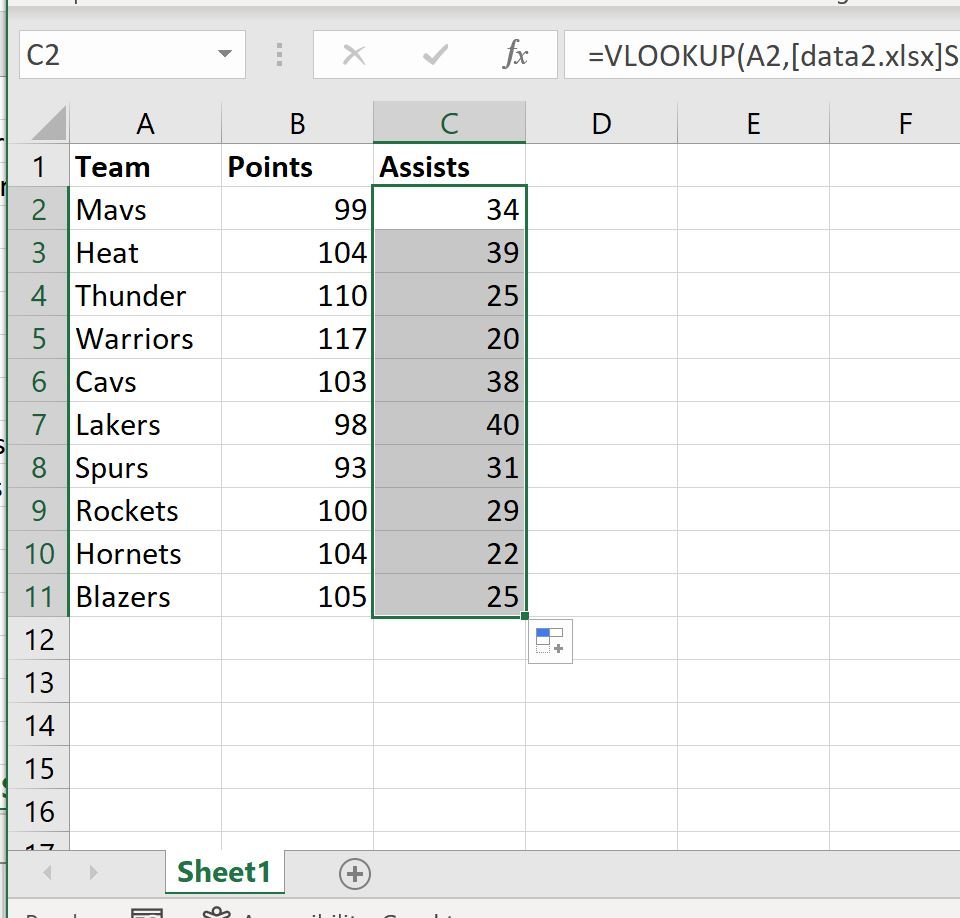
We can then drag and fill this formula down to each remaining cell in column C to find the Assists values for each team:
The values in the Assists column of the second workbook have now all been pulled into the first workbook.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common operations in Excel:
Excel: How to Find Duplicates Using VLOOKUP
Excel: How to Use VLOOKUP to Return All Matches
Excel: How to Use VLOOKUP to Return Multiple Columns