You can use the datalines statement in SAS to quickly create a new dataset from scratch.
You can use the following basic syntax to do so:
data original_data;
input var1 $ var2;
datalines;
A 12
B 19
C 23
D 40
;
run;
Here’s what each statement does:
- data: The name of the dataset
- input: The name and type of each variable in the dataset
- datalines: The actual values in the dataset
Note that a dollar sign “$” following a variable name tells SAS that the variable is a character variable.
The following examples show how to use the datalines statement in practice.
Example 1: Create Dataset with All Numeric Variables
The following code shows how to create a dataset with three numeric variables: points, assists, and rebounds:
/*create dataset*/
data original_data;
input points assists rebounds;
datalines;
22 8 4
29 5 4
31 12 8
30 9 14
22 7 1
24 9 2
18 6 4
20 5 5
25 1 4
;
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=original_data;
The result is a dataset with three numeric variables.
Example 2: Create Dataset with Character & Numeric Variables
The following code shows how to create a dataset with both character and numeric variables:
/*create dataset*/
data original_data;
input team $ position $ points assists;
datalines;
A Guard 8 4
A Guard 5 4
A Forward 12 8
A Forward 9 14
A Forward 7 1
B Guard 9 2
B Guard 14 9
B Forward 15 8
B Forward 11 4
;
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=original_data;
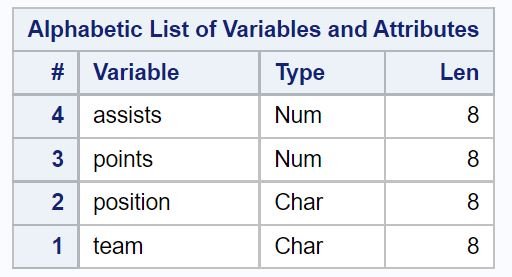
We can use the proc contents function to check the type of each variable:
proc contents data=original_data;
From the output we can see that team and position are character variables while points and assists are numeric variables.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SAS:
How to Create New Variables in SAS
How to Replace Characters in a String in SAS
How to Replace Missing Values with Zero in SAS
How to Remove Duplicates in SAS