To “normalize” a set of data values means to scale the values such that the mean of all of the values is 0 and the standard deviation is 1.
This tutorial explains how to normalize data in SAS.
Example: How to Normalize Data in SAS
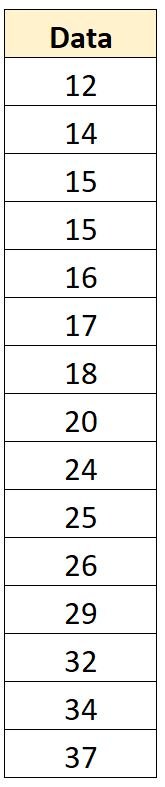
Suppose we have the following dataset:
Perform the following steps to normalize this set of data values in SAS.
Step 1: Create the Dataset
First, let’s use the following code to create the dataset in SAS:
/*create dataset*/ data original_data; input values; datalines; 12 14 15 15 16 17 18 20 24 25 26 29 32 34 37 ; run; /*view mean and standard deviation of dataset*/ proc means data=original_data Mean StdDev ndec=3; var values; run;
From the output we can see that the mean of the dataset is 22.267 and the standard deviation is 7.968.
Step 2: Normalize the Dataset
Next, we’ll use proc stdize to normalize the dataset:
/*normalize the dataset*/
proc stdize data=original_data out=normalized_data;
var values;
run;
/*print normalized dataset*/
proc print data=normalized_data;
/*view mean and standard deviation of normalized dataset*/
proc means data=normalized_data Mean StdDev ndec=2;
var values;
run;
From the output we can see that the mean of the normalized dataset is 0 and the standard deviation is 1.
Step 3: Interpret the Normalized Data
SAS used the following formula to normalize the data values:
Normalized value = (x – x) / s
where:
- x = data value
- x = mean of dataset
- s = standard deviation of dataset
Each normalized value tells us how many standard deviations the original data value was from the mean.
For example, consider the data point “12” in our original dataset. The original sample mean was 22.267 and the original sample standard deviation was 7.968.
The normalized value for “12” turned out to be -1.288, which was calculated as:
Normalized value = (x – x) / s = (12 – 22.267) / 7.968 = -1.288
This tells us that the value “12” is 1.288 standard deviations below the mean in the original dataset.
Each of the normalized values in the dataset can help us understand how close or far a particular data value is from the mean.
A small normalized value indicates that a value is close to the mean while a large normalized value indicates that a value is far from the mean.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SAS:
How to Use Proc Summary in SAS
How to Calculate Correlation in SAS
How to Create Frequency Tables in SAS