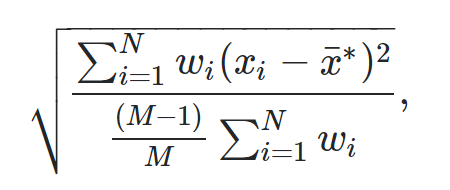The weighted standard deviation is a useful way to measure the dispersion of values in a dataset when some values in the dataset have higher weights than others.
The formula to calculate a weighted standard deviation is:
where:
- N: The total number of observations
- M: The number of non-zero weights
- wi: A vector of weights
- xi: A vector of data values
- x: The weighted mean
The following step-by-step example shows how to calculate a weighted standard deviation in Excel.
Step 1: Create the Data
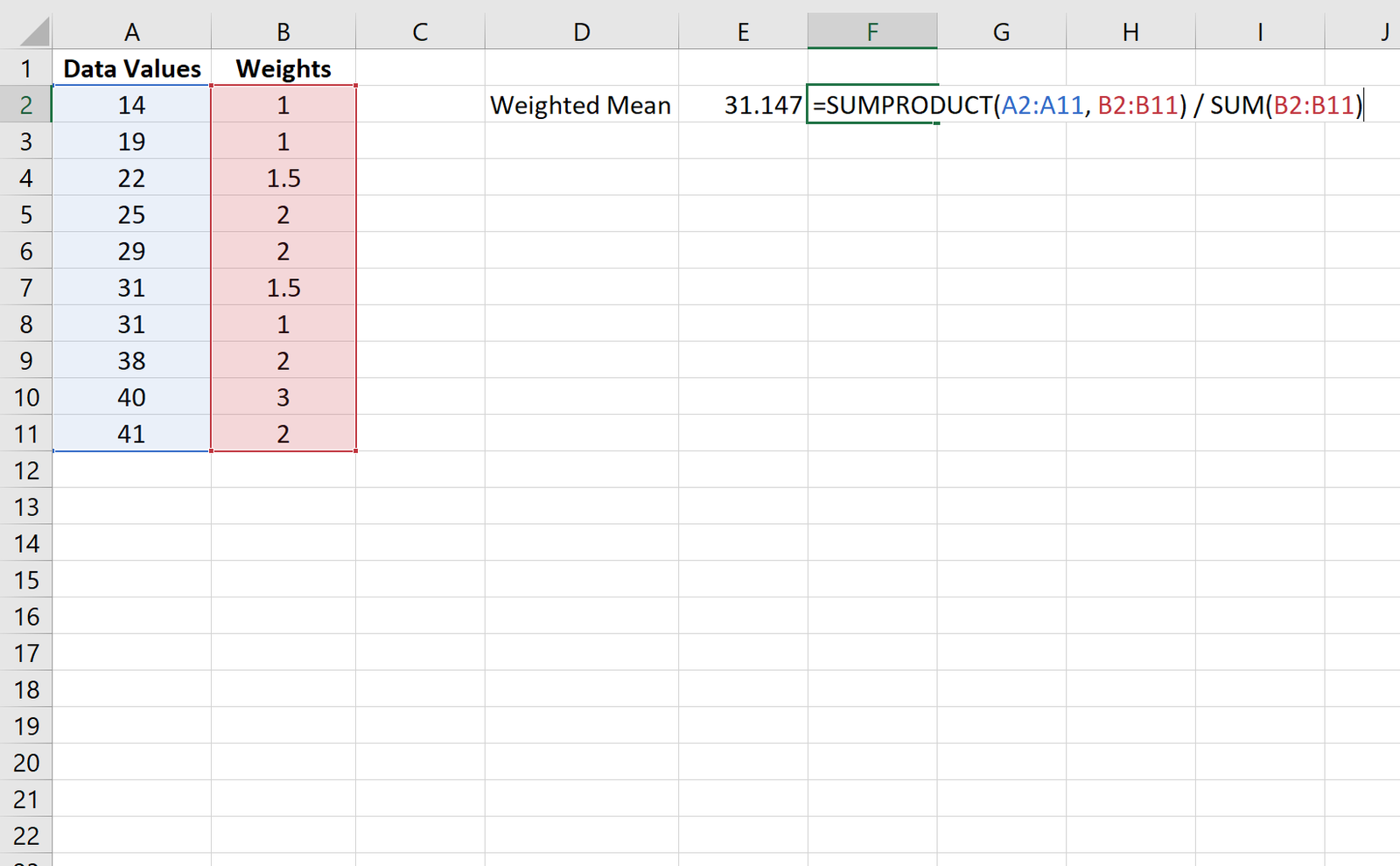
First, let’s create a column of data values along with their weights:
Step 2: Calculate the Weighted Mean
Next, we can use the following formula to calculate the weighted mean:
=SUMPRODUCT(A2:A11, B2:B11) / SUM(B2:B11)
The weighted mean turns out to be 31.147:
Step 3: Calculate the Weighted Standard Deviation
Next, we can use the following formula to calculate the weighted standard deviation:
=SQRT(SUMPRODUCT((A2:A11-E2)^2, B2:B11) / SUM(B2:B11, -1))
The weighted standard deviation turns out to be 8.570:
And if you’d like to calculate the weighted variance, it’s simply 8.5702 = 73.44.
Additional Resources
How to Calculate Weighted MAPE in Excel
How to Find Weighted Moving Averages in Excel