The mean represents the average value in a dataset. It gives us a good idea of where the center of a dataset is located.
The standard deviation represents how spread out the values are in a dataset. It gives us an idea of how closely the observations are clustered around the mean.
Using only these two values, we can understand a great deal about the distribution of values in a dataset.
To calculate the mean of a dataset in Excel, we can use the =AVERAGE(Range) function where Range is the range of values.
To calculate the standard deviation of a dataset, we can use the =STDEV.S(Range) function, where Range is the range of values.
This tutorial explains how to use these functions in practice.
Technical Note
Both the STDEV() and STDEV.S() function calculate the sample standard deviation.
You can use the STDEV.P() function to calculate the population standard deviation if your dataset represents the entire population of values.
However, in most cases we’re working with sample data rather than an entire population so we use the STDEV.S() function.
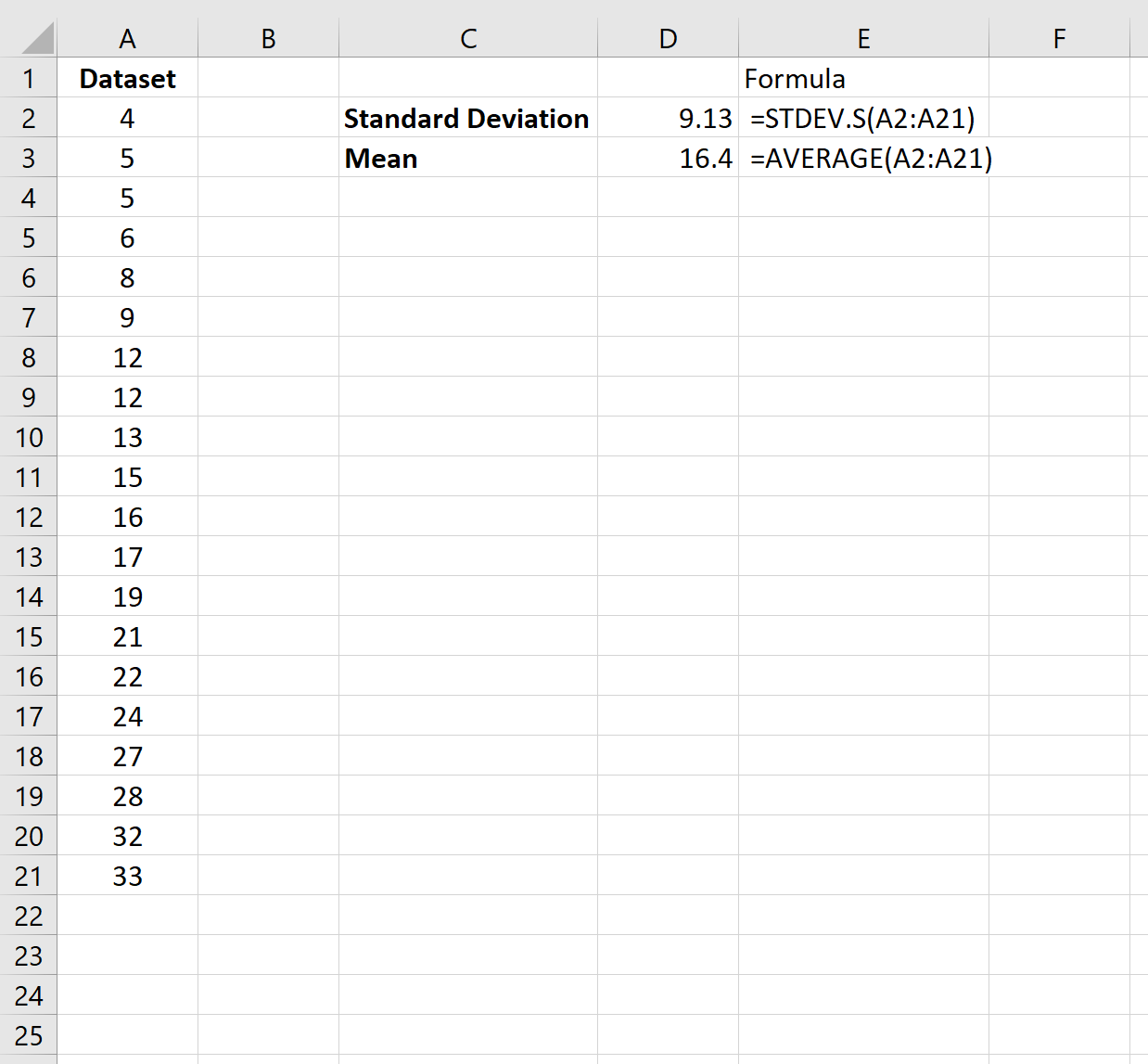
Example 1: Mean & Standard Deviation of a Single Dataset
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the mean and standard deviation of a single dataset in Excel:
The mean of the dataset is 16.4 and the standard deviation is 9.13.
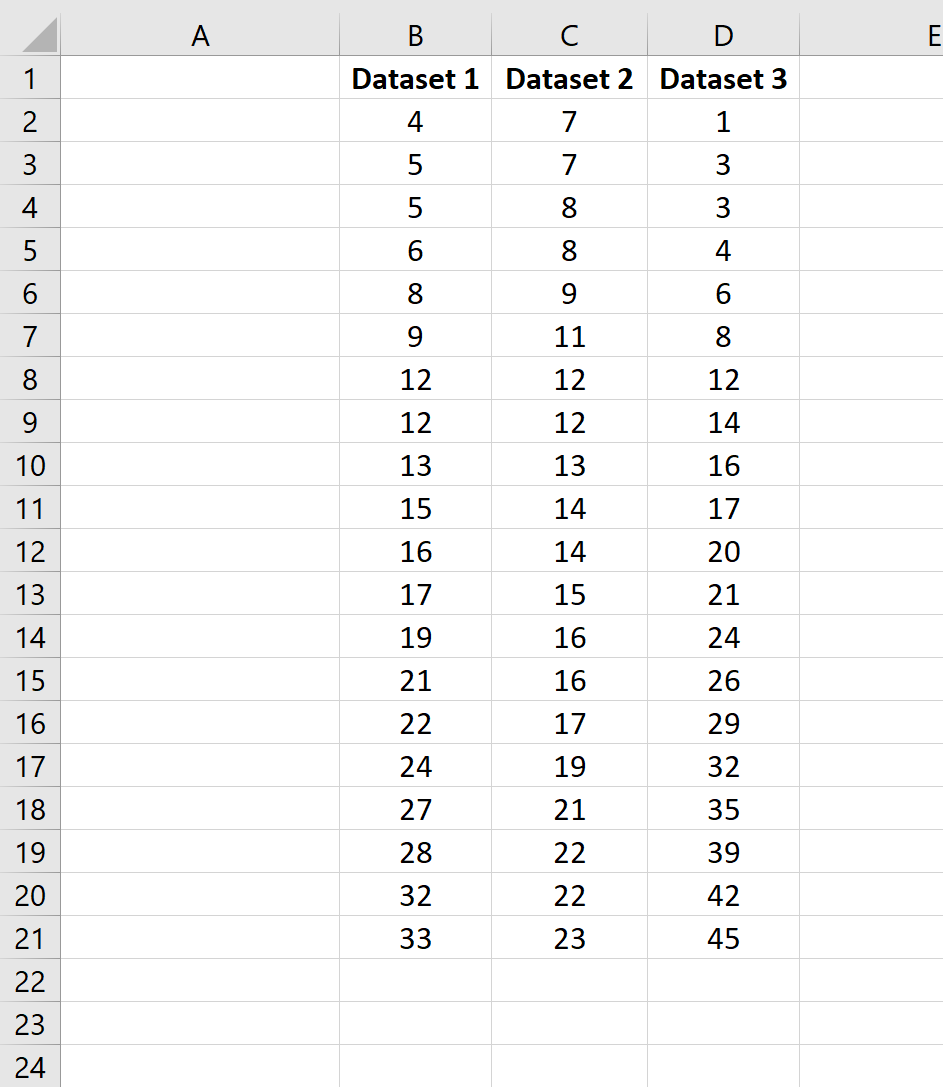
Example 2: Mean & Standard Deviation of Multiple Datasets
Suppose we have multiple datasets in Excel:
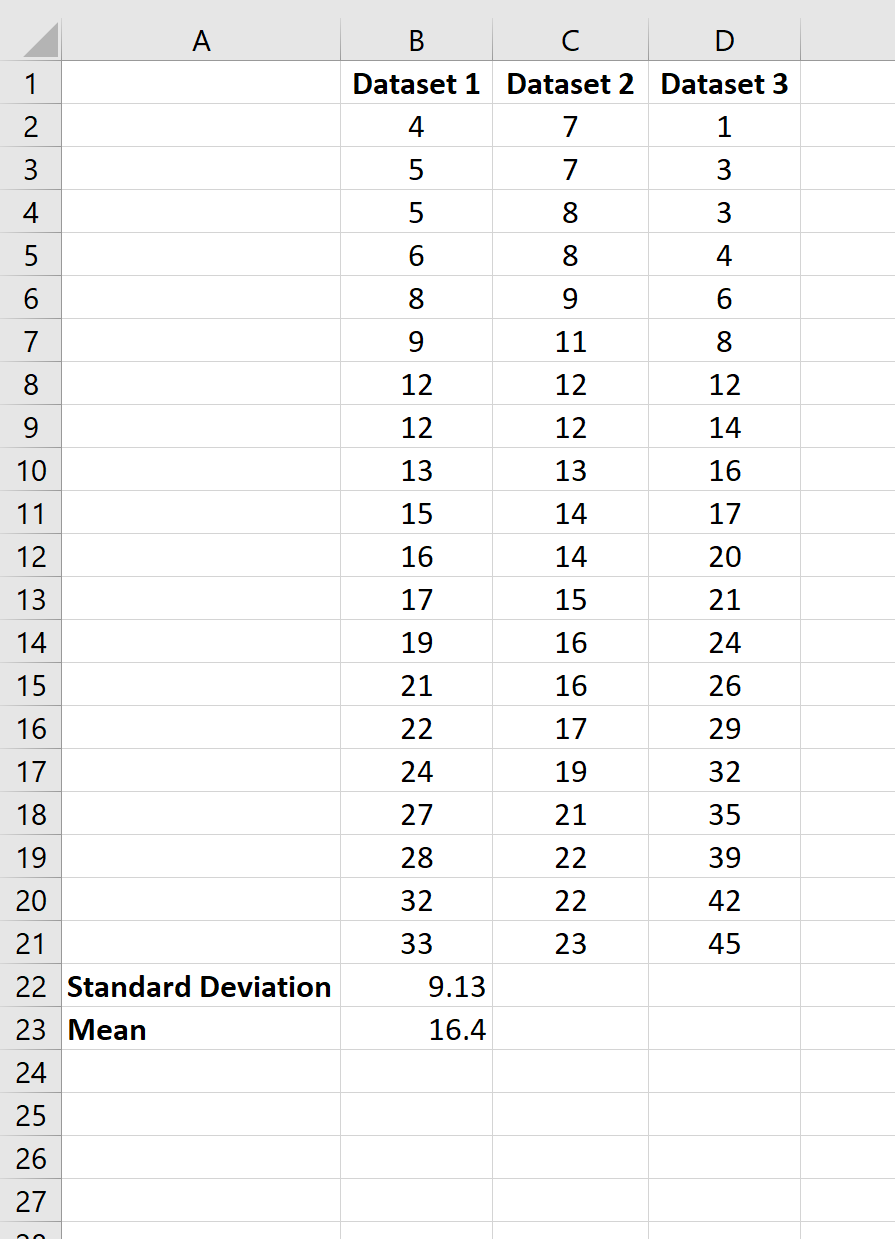
To calculate the mean and standard deviation of the first dataset, we can use the following two formulas:
- Mean: =AVERAGE(B2:B21)
- Standard Deviation: =STDEV.S(B2:B21)
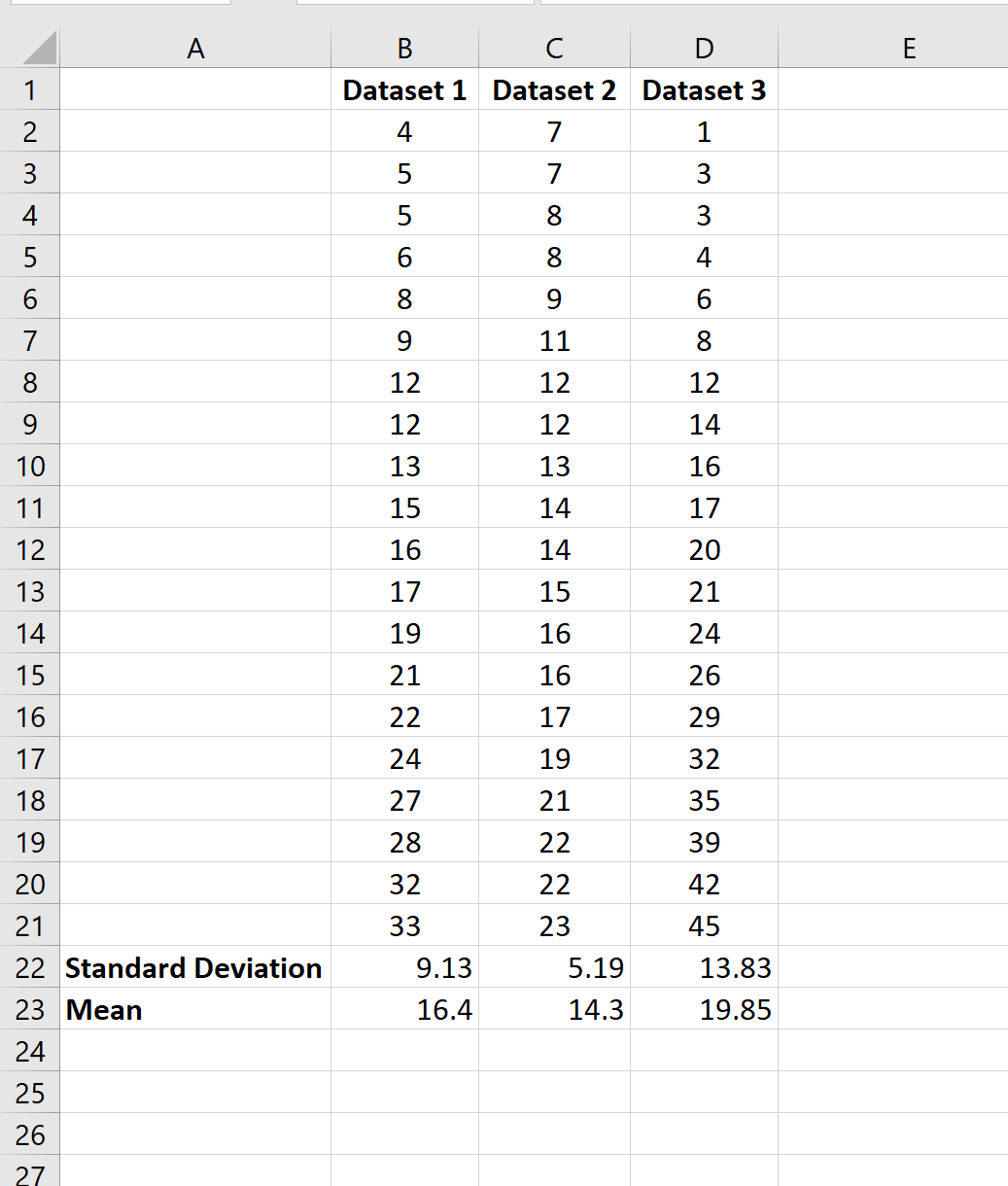
Next, we can highlight cells B22:B23 and hover over the bottom right corner of cell B23 until a tiny + appears. We can then click and drag the formulas over to the next two columns:
Additional Resources
How to Calculate a Five Number Summary in Excel
How to Calculate the Interquartile Range (IQR) in Excel
How to Calculate the Standard Error of the Mean in Excel